Java Steam流
简介
Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。
Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。
首先要澄清的是 java8 中的 Stream 与 I/O 流 InputStream 和 OutputStream 是完全不同的概念。
Stream 机制是针对集合迭代器的增强。
创建对象流的三种方式
由集合对象创建流。
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3);
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
|
数组创建流。通过静态方法 Arrays.stream() 将数组转化为流
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(new int[]{1,2,3});
|
通过静态方法 Stream.of() ,但是底层其实还是调用 Arrays.stream()
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3);
|
注意:
还有两种比较特殊的流
- 空流:Stream.empty()
- 无限流:Stream.generate() 和 **Stream.iterate()**。可以配合 limit() 使用可以限制一下数量
Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
|
流处理的特性
不存储数据
不会改变数据源
不可以重复使用
重复利用会抛出一个 IllegalStateException 的异常:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: stream has already been operated upon or closed
源数据流经管道,最后输出结果数据。
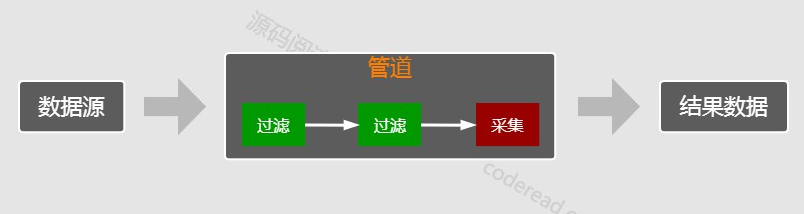
操作类型
Stream 的所有操作连起来组合成了管道,管道有两种操作:
第一种,中间操作(intermediate)。调用中间操作方法返回的是一个新的流对象。中间操作不会输出值。
第二种,终值操作(terminal)。在调用该方法后,将执行之前所有的中间操作,并返回结果。
通过连续执行多个操作倒便就组成了 Stream 中的执行管道(pipeline)。需要注意的是这些管道被添加后并不会真正执行,只有等到调用终值操作之后才会执行。
常用方法
- forEach:该方法用于对 Stream 中的每个元素进行迭代操作。
- map:该方法用于将每个元素映射到对应的结果上。
- filter:该方法用于过滤满足条件的元素。
- limit(n):获取前n个元素
- skip(n):跳过前n元素,配合limit(n)可实现分页
- sorted():自然排序,流中元素需实现Comparable接口
- sorted(Comparator com):定制排序,自定义Comparator排序器
- distinct:通过流中元素的
hashCode() 和 equals() 去除重复元素
- peek:逐个执行-中间操作
- forEach():遍历操作-终值操作
- allMatch全部符合该条件返回true
- noneMatch全部不符合该断言返回true
- anyMatch 任意一个元素符合该断言返回true
- allMatch全部符合该条件返回true
- noneMatch全部不符合该断言返回true
- anyMatch 任意一个元素符合该断言返回true
- findFirst:返回流中第一个元素
- findAny:返回流中的任意元素
- count:返回流中元素的总个数
- max:返回流中元素最大值
- min:返回流中元素最小值
- limit skip distinct sorted 都是有状态操作,这些操作只有拿到前面处理后的所有元素之后才能继续下去。
举例
Apply实体类
class Apple{
private Integer appleId;
private String appleName;
private String location;
private Integer weight;
public Apple(Integer appleId, String appleName, String location, Integer weight) {
this.appleId = appleId;
this.appleName = appleName;
this.location = location;
this.weight = weight;
}
|
流实现举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Apple> collect = list.stream().filter(apple -> apple.weight > 5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
List<String> names = list.stream().map(apple -> apple.appleName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
List<String> distinctName = names.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(distinctName);
list.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
list.stream().filter(apple -> apple.getAppleName().equals("青苹果"))
.peek(apple -> System.out.println("苹果筛选1:"+ apple))
.filter(apple -> apple.getWeight()>5)
.peek(apple -> System.out.println("苹果筛选2:"+ apple))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
long count = list.parallelStream().filter(apple -> apple.getLocation().equals("广东")).count();
System.out.println(count);
Stream.iterate(0,x->x+2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
String merge = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(merge);
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(9,6,5,3,9,7,10,5,5,4,6);
IntSummaryStatistics stats = numbers.stream().mapToInt((x) -> x).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("列表中最大的数 : " + stats.getMax());
System.out.println("列表中最小的数 : " + stats.getMin());
System.out.println("所有数之和 : " + stats.getSum());
System.out.println("平均数 : " + stats.getAverage());
Stream<String> stringStream = strings.stream().flatMap(s -> {
String[] split = s.split(",");
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(split).filter(x -> !x.isEmpty());
return stream;
});
System.out.println(stringStream.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
|
版权声明: 此文章版权归Chankeitin所有,如有转载,请註明来自原作者











